A new study by Professor Li Taisheng’s team at the Department of Infectious Diseases, PUMCH has shown that (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide, the national Class I new drug developed by modifying the traditional Chinese medicine Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F (TwHF), is effective in boosting CD4+ T cell count in HIV patients with poor immune reconstitution after long-term antiretroviral therapy. The findings of this study have recently published online in The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, representing a major breakthrough in addressing the tough issue of incomplete immune reconstitution in HIV infections.

HIV mainly attacks CD4+ T cells of the human immune system. Around 20–30% of HIV patients receiving effective antiretroviral therapy fail to achieve optimal immune reconstitution, and they are called immunological non-responders (INRs). Over the past 15 years, Li Taisheng’s team has been using the traditional Chinese medicine TwHF (“Leigongteng”) to control inflammation and improve immune reconstitution. The team has achieved initial clinical efficacy and also vigorously explored the pharmacological mechanism.
However, most of the Leigongteng preparations on the market are naturally extracted TwHF coformulation, which consists of unfixed compositions. Shanghai Pharmaceuticals Holding Co., Ltd. (SPH) has successfully solved this problem by modifying the main bioactive component triptolide into a novel compound (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8, Leitengshu) with immunosuppressive activity and reduced toxicity, creating a new class I chemical drug with fixed composition and intellectual property rights.
PUMCH and SPH jointly conducted a multi-center clinical trial: “(5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide for HIV immunological non-responders receiving ART: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase II study”.. The results showed that orally administering LLDT-8 1mg daily for 48 weeks significantly increased peripheral CD4+ T-cell count in HIV patients with incomplete immune reconstitution (63/mm3), significantly higher than those in the placebo group (32/mm3) and the low-dose (0.5mg LLDT-8) group (49/mm3), with an even greater CD4+ T-cell recovery in those over 45 years old, up to 96/mm3. Meanwhile, Leitengshu significantly reduced inflammation levels in participants, and the incidence of adverse events was similar between the groups.
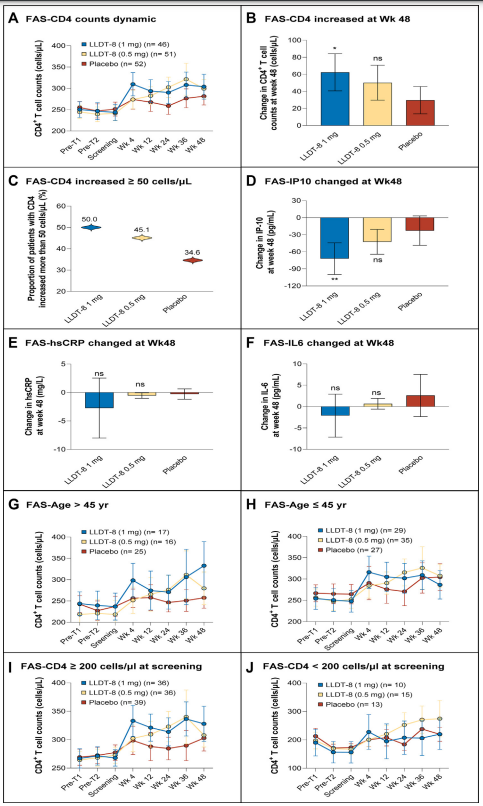
▲The CD4+ T-cell recovery and cytokine changes among FAS population
Hema Urban, Senior Editor at “The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific”, spoke highly of the research outcome: Leitengshu is the only drug that has so far been shown by rigorous clinical studies to help improve incomplete immune reconstitution in HIV infections. Meanwhile, the R&D process of Leitengshu compliant with modern drug evaluation methods provides valuable experience that will help more traditional Chinese medicine gain international recognition.
Written by Cao Wei
Edited by Gan Dingzhu
Translated by Liu Haiyan
Edited by Xie Jing and Wang Yao
